flux数据流在rn中的使用
flux介绍
flux是Facebook提出的react开发单向数据流的模式,在实际开发过程做看过很多逻辑混乱,flux可以很大程度解决这一的问题不仅如此,这种设计模式在其他的项目结构中任然很有用。
网上很多文章都是在react中使用flux,放到react-native中各种出错,本文针对react-native。
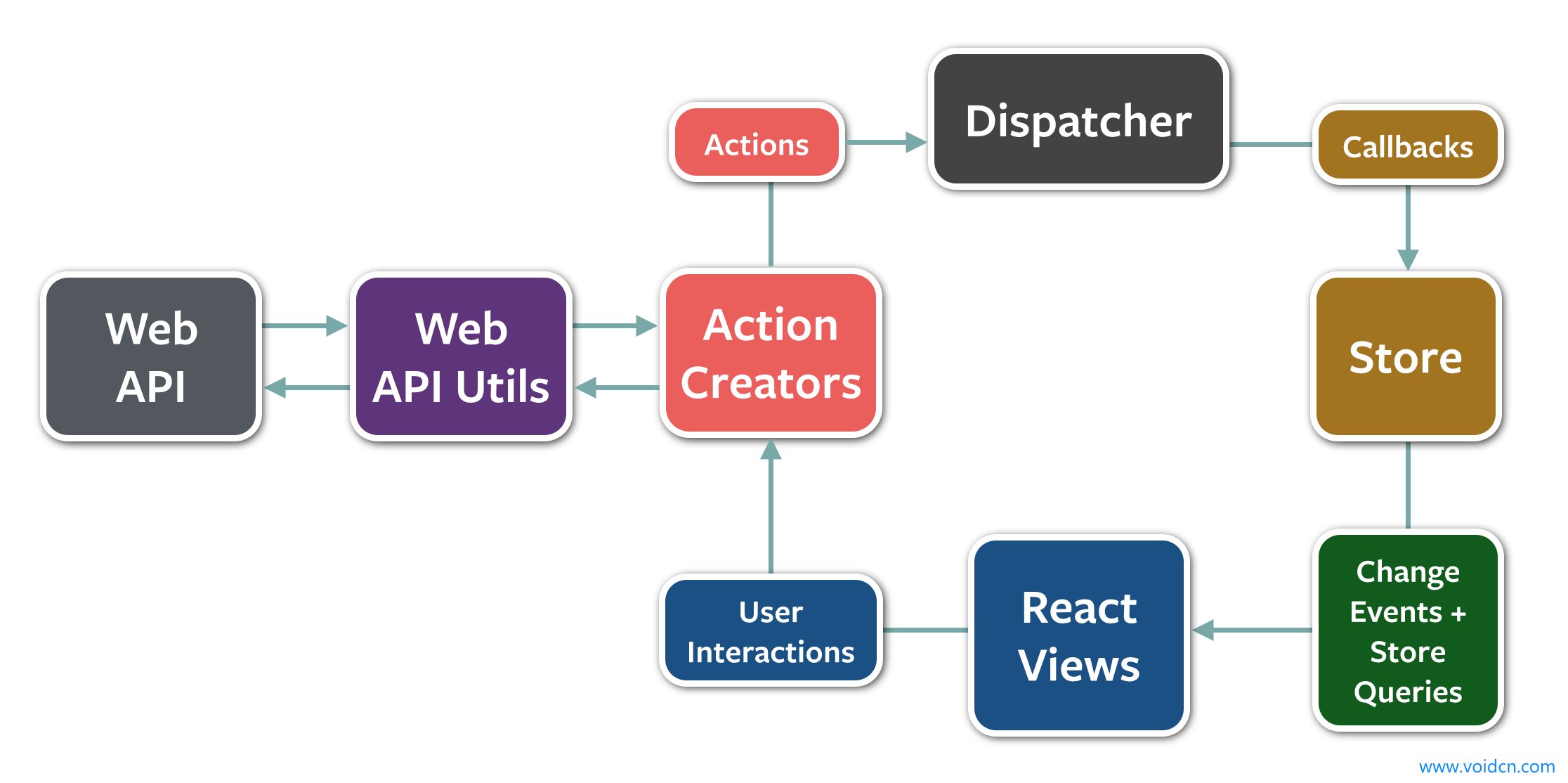
flux主要分成4个模块
the dispatcher
处理动作分发,维护 Store 之间的依赖关系
the stores
数据和逻辑部分
the views
React 组件,这一层可以看作 controller-views,作为视图同时响应用户交互
the actions
提供给 dispatcher 传递数据给 store
数据的流向
Action -> Dispatcher -> Store -> View
flux的详细概念可以参考这两篇文章
上面的介绍很详细,我就不重复造轮子了,但是有个问题,上面的都是基于react的demo,在react-native中会出现很多问题,主要问题是?
demo
controller层
controller.js 页面, 与view,actions,store 交互,controller有几个作用
- 视图展示,渲染
- 发出视图交互事件,但不处理交互事件
- 订阅store的改变等通知,根据通知处理视图,但不处理数据
//view
var someview = require('./RecipesAction');
//actions
var actions = require('./RecipesAction');
//store
var store = require('./RecipesStore.js');
var Recipes = React.createClass({
componentDidMount: function() {
//添加监听作为测试
store.addTestListener(this.test);
//初始化数据
actions.initRecipes();
}
render() {
return (
<someview></someview>
);
....
);
actions层
actions负责只负责通过dispatcher把事件派发出去,但不处理事件。
var dispatcher = require('../../AppDispatcher.js');
var ButtonActions = {
initRecipes: function (text) {
dispatcher.dispatch({
actionType: 'init_recipes',
});
},
};
module.exports = ButtonActions;
dispatcher
dispatcher负责处理事件调度,注册和事件委托,派送事件等,在rn中有2个文件就可以完成,
文件dispatcher.js 比较长,大家随意看看,源码解释可以参考:- Flux源码解析(一)
dispatcher.js 文件引用了 invariant ,这个只是一个工具,作为错误消息提示。
这两个文件从react版本中移过来,只是做了简单的修改,可以见文章最后的附录
store
store是数据实体,并保护数据修改的委托实现。
通过dispatcher.register方法注册dispatcher的listener, 类对象使用RCTDeviceEventEmitter对象进行事件转发。
//成功
var dispatcher = require('../../AppDispatcher.js');
import React, {
Text,
View
} from 'react-native';
var EventEmitter = require('RCTDeviceEventEmitter');
var TEST_EVENT = 'test';
var RecipesStore = {
items: [],
fliter:{},
init: function() {
EventEmitter.emit("test");
},
addTestListener:function(cb){
EventEmitter.addListener(TEST_EVENT, cb);
},
};
dispatcher.register(function(action){
switch(action.actionType){
case 'init_recipes' :
RecipesStore.init();
default: //no op
}
});
module.exports = RecipesStore;
参考
最后
感谢收看,如果对大家有帮助,请github上follow和star,本文发布在刘彦玮的技术博客,转载请注明出处
附录
Dispatcher.js
/**
* Copyright (c) 2014-2015, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*
* @providesModule Dispatcher
* @flow
* @preventMunge
*/
'use strict';
var invariant = require('./invariant');
export type DispatchToken = string;
var _prefix = 'ID_';
/**
* Dispatcher is used to broadcast payloads to registered callbacks. This is
* different from generic pub-sub systems in two ways:
*
* 1) Callbacks are not subscribed to particular events. Every payload is
* dispatched to every registered callback.
* 2) Callbacks can be deferred in whole or part until other callbacks have
* been executed.
*
* For example, consider this hypothetical flight destination form, which
* selects a default city when a country is selected:
*
* var flightDispatcher = new Dispatcher();
*
* // Keeps track of which country is selected
* var CountryStore = {country: null};
*
* // Keeps track of which city is selected
* var CityStore = {city: null};
*
* // Keeps track of the base flight price of the selected city
* var FlightPriceStore = {price: null}
*
* When a user changes the selected city, we dispatch the payload:
*
* flightDispatcher.dispatch({
* actionType: 'city-update',
* selectedCity: 'paris'
* });
*
* This payload is digested by `CityStore`:
*
* flightDispatcher.register(function(payload) {
* if (payload.actionType === 'city-update') {
* CityStore.city = payload.selectedCity;
* }
* });
*
* When the user selects a country, we dispatch the payload:
*
* flightDispatcher.dispatch({
* actionType: 'country-update',
* selectedCountry: 'australia'
* });
*
* This payload is digested by both stores:
*
* CountryStore.dispatchToken = flightDispatcher.register(function(payload) {
* if (payload.actionType === 'country-update') {
* CountryStore.country = payload.selectedCountry;
* }
* });
*
* When the callback to update `CountryStore` is registered, we save a reference
* to the returned token. Using this token with `waitFor()`, we can guarantee
* that `CountryStore` is updated before the callback that updates `CityStore`
* needs to query its data.
*
* CityStore.dispatchToken = flightDispatcher.register(function(payload) {
* if (payload.actionType === 'country-update') {
* // `CountryStore.country` may not be updated.
* flightDispatcher.waitFor([CountryStore.dispatchToken]);
* // `CountryStore.country` is now guaranteed to be updated.
*
* // Select the default city for the new country
* CityStore.city = getDefaultCityForCountry(CountryStore.country);
* }
* });
*
* The usage of `waitFor()` can be chained, for example:
*
* FlightPriceStore.dispatchToken =
* flightDispatcher.register(function(payload) {
* switch (payload.actionType) {
* case 'country-update':
* case 'city-update':
* flightDispatcher.waitFor([CityStore.dispatchToken]);
* FlightPriceStore.price =
* getFlightPriceStore(CountryStore.country, CityStore.city);
* break;
* }
* });
*
* The `country-update` payload will be guaranteed to invoke the stores'
* registered callbacks in order: `CountryStore`, `CityStore`, then
* `FlightPriceStore`.
*/
class Dispatcher<TPayload> {
_callbacks: {[key: DispatchToken]: (payload: TPayload) => void};
_isDispatching: boolean;
_isHandled: {[key: DispatchToken]: boolean};
_isPending: {[key: DispatchToken]: boolean};
_lastID: number;
_pendingPayload: TPayload;
constructor() {
this._callbacks = {};
this._isDispatching = false;
this._isHandled = {};
this._isPending = {};
this._lastID = 1;
}
/**
* Registers a callback to be invoked with every dispatched payload. Returns
* a token that can be used with `waitFor()`.
*/
register(callback: (payload: TPayload) => void): DispatchToken {
var id = _prefix + this._lastID++;
this._callbacks[id] = callback;
return id;
}
/**
* Removes a callback based on its token.
*/
unregister(id: DispatchToken): void {
invariant(
this._callbacks[id],
'Dispatcher.unregister(...): `%s` does not map to a registered callback.',
id
);
delete this._callbacks[id];
}
/**
* Waits for the callbacks specified to be invoked before continuing execution
* of the current callback. This method should only be used by a callback in
* response to a dispatched payload.
*/
waitFor(ids: Array<DispatchToken>): void {
invariant(
this._isDispatching,
'Dispatcher.waitFor(...): Must be invoked while dispatching.'
);
for (var ii = 0; ii < ids.length; ii++) {
var id = ids[ii];
if (this._isPending[id]) {
invariant(
this._isHandled[id],
'Dispatcher.waitFor(...): Circular dependency detected while ' +
'waiting for `%s`.',
id
);
continue;
}
invariant(
this._callbacks[id],
'Dispatcher.waitFor(...): `%s` does not map to a registered callback.',
id
);
this._invokeCallback(id);
}
}
/**
* Dispatches a payload to all registered callbacks.
*/
dispatch(payload: TPayload): void {
invariant(
!this._isDispatching,
'Dispatch.dispatch(...): Cannot dispatch in the middle of a dispatch.'
);
this._startDispatching(payload);
try {
for (var id in this._callbacks) {
if (this._isPending[id]) {
continue;
}
this._invokeCallback(id);
}
} finally {
this._stopDispatching();
}
}
/**
* Is this Dispatcher currently dispatching.
*/
isDispatching(): boolean {
return this._isDispatching;
}
/**
* Call the callback stored with the given id. Also do some internal
* bookkeeping.
*
* @internal
*/
_invokeCallback(id: DispatchToken): void {
this._isPending[id] = true;
this._callbacks[id](this._pendingPayload);
this._isHandled[id] = true;
}
/**
* Set up bookkeeping needed when dispatching.
*
* @internal
*/
_startDispatching(payload: TPayload): void {
for (var id in this._callbacks) {
this._isPending[id] = false;
this._isHandled[id] = false;
}
this._pendingPayload = payload;
this._isDispatching = true;
}
/**
* Clear bookkeeping used for dispatching.
*
* @internal
*/
_stopDispatching(): void {
delete this._pendingPayload;
this._isDispatching = false;
}
}
module.exports = Dispatcher;
invariant.js
/**
* Copyright 2013-2015, Facebook, Inc.
* All rights reserved.
*
* This source code is licensed under the BSD-style license found in the
* LICENSE file in the root directory of this source tree. An additional grant
* of patent rights can be found in the PATENTS file in the same directory.
*/
'use strict';
/**
* Use invariant() to assert state which your program assumes to be true.
*
* Provide sprintf-style format (only %s is supported) and arguments
* to provide information about what broke and what you were
* expecting.
*
* The invariant message will be stripped in production, but the invariant
* will remain to ensure logic does not differ in production.
*/
var NODE_ENV = process.env.NODE_ENV;
var invariant = function(condition, format, a, b, c, d, e, f) {
if (NODE_ENV !== 'production') {
if (format === undefined) {
throw new Error('invariant requires an error message argument');
}
}
if (!condition) {
var error;
if (format === undefined) {
error = new Error(
'Minified exception occurred; use the non-minified dev environment ' +
'for the full error message and additional helpful warnings.'
);
} else {
var args = [a, b, c, d, e, f];
var argIndex = 0;
error = new Error(
format.replace(/%s/g, function() { return args[argIndex++]; })
);
error.name = 'Invariant Violation';
}
error.framesToPop = 1; // we don't care about invariant's own frame
throw error;
}
};
module.exports = invariant;
